The Industrial Revolution, a period of immense technological advancements and social transformation, marks a pivotal turning point in human history. It laid the groundwork for modern industrial societies and shaped the world as we know it today. But where did this revolutionary movement begin? Delving into the origins of the Industrial Revolution is like embarking on a captivating journey back in time, unraveling the layers of innovation and change that swept across nations. While often associated with Britain’s rise to global power during the 18th and 19th centuries, tracing its roots reveals a more nuanced narrative that encompasses multiple countries and regions. In order to grasp the true beginnings of this epochal event, we must explore various factors such as technology, resources, economic conditions, and societal shifts that converged to ignite this remarkable era of progress.
Pre-Industrial Era:
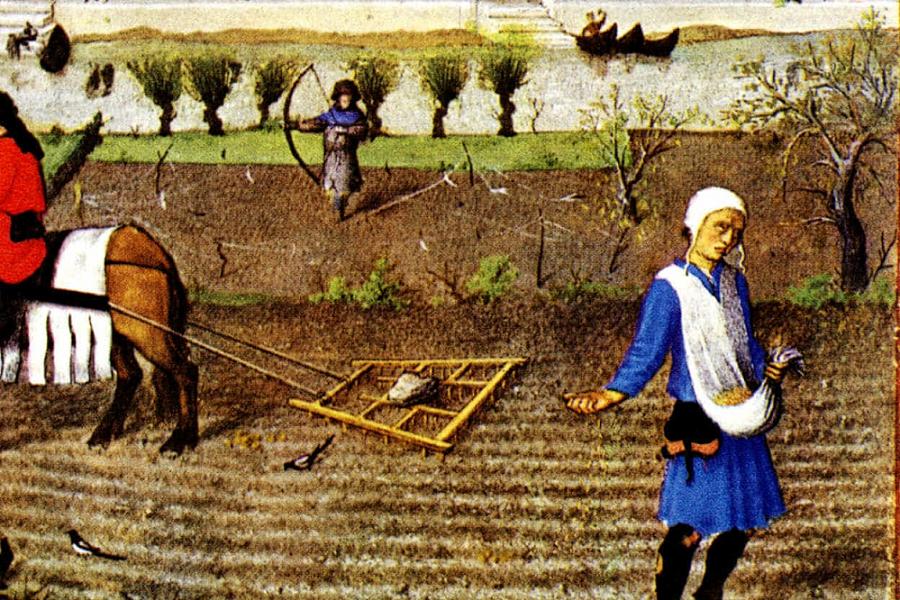

The Pre-Industrial Era, also known as the Agricultural Society, was characterized by the dominance of agriculture and cottage industries. This period laid the foundation for the Industrial Revolution to take place. During this time, farming and agricultural practices were at the core of society, with most people living in rural areas and relying on subsistence farming for survival.
- In addition to farming, cottage industries thrived during this era. These industries included activities such as weaving, spinning, and pottery making. They were typically carried out in homes or small workshops within communities. Cottage industries provided a way for families to supplement their income and produce goods that could be sold locally or traded with neighboring towns.
- The Agricultural Society not only laid the groundwork for technological advancements but also shaped social structures. The majority of individuals lived in small villages or on farms, working together to cultivate land and raise livestock. This sense of community fostered strong interdependent relationships among neighbors.
- As we reflect upon this era today, it is important to grasp its significance in setting the stage for industrialization as we know it today. The rise of agriculture gave humans greater control over food production, creating surplus that allowed some individuals to specialize in other crafts beyond just farming. Furthermore, cottage industries served as vital sources of innovation and trade within local communities.
The Birth Of The Factory System In Britain

The birth of the factory system in Britain marked a pivotal moment in history, igniting the flames of the Industrial Revolution. It was during the late 18th century that a series of significant technological advancements and social changes came together to transform traditional methods of production. The factory system not only revolutionized manufacturing but also had far-reaching effects on society as a whole.
- One key aspect that fueled the rise of factories was the development of new machinery, such as James Watt’s steam engine. This invention allowed for increased efficiency and productivity by replacing human and animal labor with mechanical power. Alongside this, advancements in textile machinery like Richard Arkwright’s water frame enabled mass production on an unprecedented scale, laying the foundations for future industrial growth.
- Another pivotal factor contributing to the emergence of factories was a shift from home-based artisan work to centralized production centers. This transition was driven by various factors, including economic pressures that required larger quantities of goods to be produced at lower costs. Consequently, skilled craftsmen were forced into wage labor within factory walls, marking an irreversible societal change.
In conclusion, the birth of the factory system in Britain symbolized a turning point in history characterized by profound transformations in technology and social organization. Steam engines and textile machinery ushered in an age where mechanization ruled over manual labor. Moreover, these technological advancements led to centralization and concentration of production activities within factories, forever altering how goods were manufactured.
The Role Of Steam Power And Inventions

The role of steam power and inventions cannot be overstated when examining the origins of the Industrial Revolution. Steam power, fueled by coal, revolutionized transportation and manufacturing processes, laying the foundation for unprecedented economic growth. The invention of the steam engine by James Watt in the late 18th century truly transformed society as it enabled factories to produce goods at an unprecedented rate while also facilitating long-distance travel through the creation of steam-powered locomotives.
It is important to note that the development and widespread adoption of other key inventions during this time period played a pivotal role as well. Innovative technologies such as the spinning jenny, which allowed for mass production of textiles, or Eli Whitney’s cotton gin, which revolutionized cotton processing, all contributed to driving productivity levels upwards. This influx of new ideas not only accelerated industrialization but also spurred further innovation across various industries. As inventions improved efficiency and lowered costs through automation, businesses found new ways to expand their operations and meet increasing demands.
Spread Of Industrialization To Europe And North America
Europe and North America were at the forefront of the spread of industrialization in the 18th and 19th centuries, a period that would come to be known as the Industrial Revolution. While many believe that this revolutionary era originated solely in Britain, it quickly expanded its influence across the Atlantic, transforming these regions into major centers of industrial growth.
- In Europe, countries like Germany and France embraced industrialization with great enthusiasm. Germany, in particular, emerged as a formidable force in industries such as steel production and engineering. Its success can be attributed to various factors such as abundant natural resources, a skilled workforce, and significant investments in infrastructure.
- Likewise, North America experienced significant industrial expansion during this time. The United States took advantage of its vast landmass and natural resources to fuel rapid economic development. Cities like Chicago became bustling centers of trade and commerce while companies like Ford revolutionized transportation with their automobile innovations.
- The spread of industrialization created not only economic prosperity but also profound social changes. The emergence of the working-class led to unprecedented urbanization as people flocked to cities searching for employment opportunities. However, alongside progress came challenges such as poor working conditions and inequality among workers.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, it is clear that the industrial revolution had a profound global impact. While it may have started in Britain, its effects were felt far beyond its borders. The revolutionary changes in manufacturing methods and technological advancements spread to other countries, transforming their economies and societies.
One of the key ways in which the industrial revolution had a global impact was through the expansion of trade networks. As goods were produced on a larger scale and more efficiently, they could be transported across long distances, creating new opportunities for global trade. This led to an increase in economic interconnectedness between nations and ultimately laid the foundation for today’s globalized economy.
Furthermore, the industrial revolution also spurred social and political changes around the world. As people flocked to factories seeking employment opportunities, urbanization became a common phenomenon. This shift from rural agrarian lifestyles to urban living transformed traditional social structures and created new challenges and opportunities for governments.
Overall, understanding the global impact of the industrial revolution is essential for comprehending our modern world. It not only shaped economies but also influenced how we live and interact with one another today.
Also Read: How To Paint A Room With A view




